Developer Guide
Table of contents
- Acknowledgements
- Setting up, getting started
- Design
- Documentation, logging, testing
- Implementation
- Appendix: Requirements
- Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Acknowledgements
The documentation and class organization of this project is done with some reference to the AB-3 repository.
Setting up, getting started
Prerequisites: JDK 11 (use the exact version), update Intellij to the most recent version.
- Ensure Intellij JDK 11 is defined as an SDK, as described here – this step is not needed if you have used JDK 11 in a previous Intellij project.
- In the same dialog, you may have to set the Project language level field to the SDK default option.
-
Import the project as a Gradle project, as described here.
- Verify the setup: After the importing is complete, locate the
src/main/java/seedu/duke/Duke.javafile, right-click it, and chooseRun Duke.main(). If the setup is correct, you should see something like the below:
> Task :compileJava UP-TO-DATE
> Task :processResources UP-TO-DATE
> Task :classes UP-TO-DATE
> Task :Duke.main()
_______________________________________________________________________________
I can't retrieve the saved task data. Creating new file..
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
I can't retrieve the saved lesson data. Creating new file..
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
I can't retrieve the saved module data. Creating new file..
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_ _ _ _ ____ ____ _ _ ____ ____ __ __
| \ |"| U |"|u| | / __"| u U | __")uU |"|u| | | _"\ | _"\ \ \ / /
<| \| |> \| |\| |<\___ \/ \| _ \/ \| |\| |/| | | | /| | | | \ V /
U| |\ |u | |_| | u___) | | |_) | | |_| |U| |_| |\U| |_| |\U_|"|_u
|_| \_| <<\___/ |____/>> |____/ <<\___/ |____/ u |____/ u |_|
|| \\,-.(__) )( )( (__) _|| \\_ (__) )( |||_ |||_ .-,//|(_
(_") (_/ (__) (__) (__) (__) (__) (__)_) (__)_) \_) (__)
_______________________________________________________________________________
Follow this guide to set up Intellij IDEA to the coding style that matches ours.
Design
Architecture
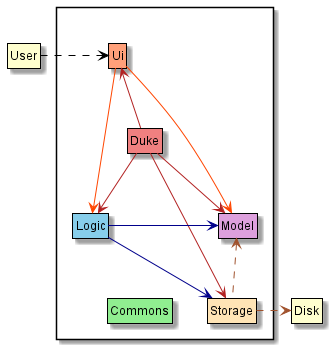
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
📝 Note:
DukeExceptionclass is not shown in the diagram for simplicity’s sake.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main has two classes called Duke and DukeException.
Duke is responsible for:
- At app launch: Initializes the components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down: Shuts down the components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
DukeException is responsible for:
- Manages Duke-related exceptions.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
The rest of the App consists of four components.
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The parser and command executor.Model: Holds the various data structures of the App.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
How the architecture components interact with each other
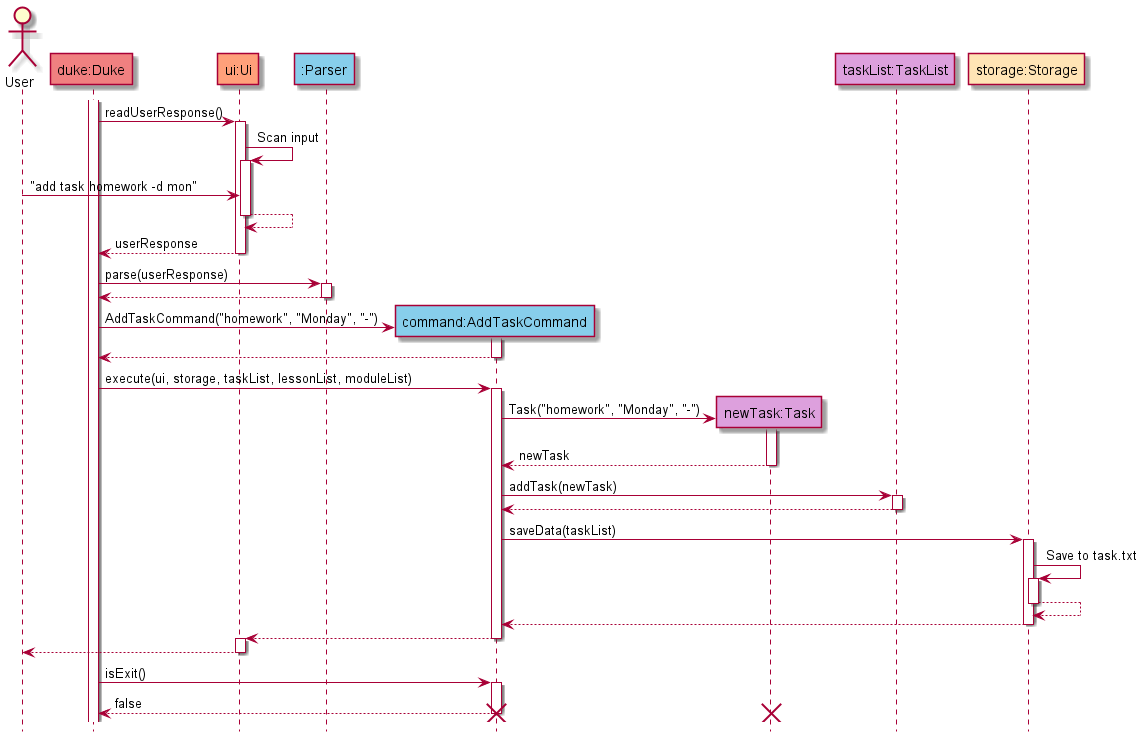
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the
user issues the command add task homework -d mon.
UI component
API : Ui.java
The Ui component contains:
- the method
readUserResponse()to read from the standard input. - methods to print messages as strings to the standard output.
- constant strings, such as
LINEandPADDING, which are used to format the printed messages.
The methods in the Ui component may call methods from TaskList, LessonList or ModuleList to get information from the respective components.
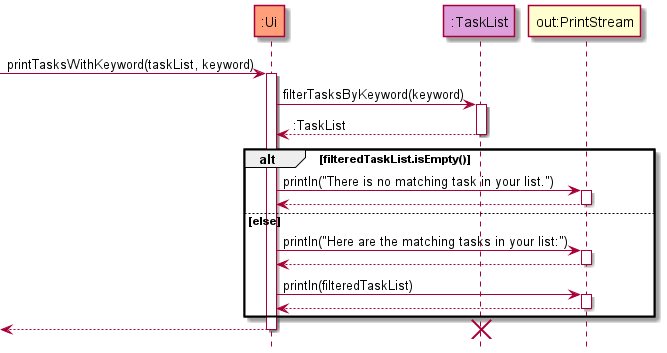
Printing tasks containing a keyword:
Logic component
Here is the class diagram of the Logic component:
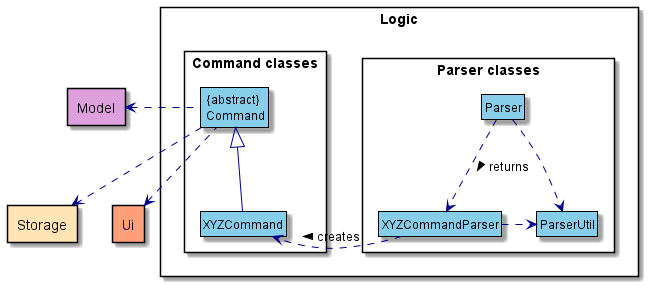
📝 Note: XYZ is a placeholder for specific command name (e.g., AddModuleCommand).
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it uses theParserclass to parse the user command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g., AddModuleCommand) which is then executed. - The
Commandcan communicate with theModelclass when it is executed (e.g. to add a module). - If the operations above are successful, the
Commandwill save theModeldata by using theStorageclass. - The result is then printed to user by the
Uiclass.
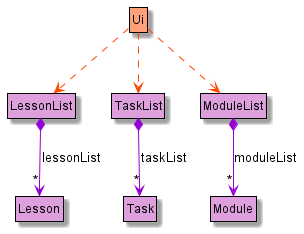
Model component
The model package consists of three components: Lesson, Task and Module.
Lesson component
API : Lesson.java
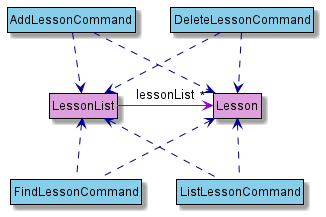
The Lesson component
- stores data specific to a lesson as entered by the user
- stores all
Lessonobjects created by user commands in aLessonListobject - does not depend on any of the other three components
Module component
API Module.java
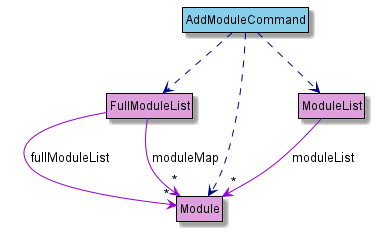
The Module component,
- stores information regarding modules added by the user and on the NUSMods API
- does not depend on any of the other three components
FullModuleListstores allModuleobjects corresponding to the modules found on NUSModsModuleListstores all user-addedModuleobjects
Task Component
API Task.java
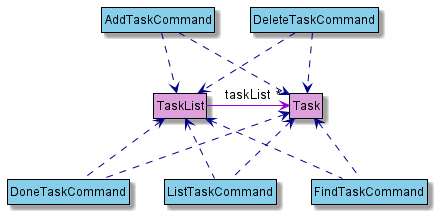
The Task component,
- stores data specific to a task as entered by the user
- stores all
Taskobjects as created by user commands in aTaskListobject - does not depend on any of the other three components
Storage component
API : Storage.java
The Storage component makes use of the serializing methods in the TaskList, LessonList, and ModuleList classes to save data to the data folder.
It also reads data from a given path into strings which can be utilized by those 3 list classes to create a list.
The Storage component has methods that:
- create the files
task.txt,lesson.txt,module.txtin thedatafolder. - load data from the file in the given path into an array of strings representing each line of data.
- save data of a given list by overwriting the respective file in the
datafolder with serialized data.
The following sequence diagrams show how task data is saved and loaded using the Storage class.
Common classes
The “Commons” folder stores classes that assist in the functioning of the various features of the application.
Core
- The
CommandFlagclass- stores string constants representing flags to be used in user inputs.
- The
CommandFormatclass- stores string constants representing formats for user commands.
- provides a method that creates a ready-to-print string that suggests selected command formats for the user.
- The
CommandTypeclass- stores enumerations for command types.
- provides a method to convert a command word into a
CommandType.
- The
DayOfTheWeekclass- stores enumerations for the Day of the Week.
- provides methods to check the validity of a Day of the Week input and convert it into a
DayOfTheWeek.
- The
Gradeclass- stores a predefined array of possible grades.
- provides a method to check the validity of a Grade input.
- The
Messagesclass- stores string constants for simple success and error messages to be printed to users. (usually 1 liners)
- The
Priorityclass- stores enumerations for task priority.
- provides methods to check the validity of a priority input and convert it into a
Priority.
Utility
-
The
DayUtilclass contains utility methods that makes use of theDayOfTheWeekvariable of a class. -
The
JsonUtilclass contains utility methods that make use of theModuleInfo.Jsonfile. -
The
LinkUtilclass contains utility methods that help in launching URLs. -
The
StringUtilclass contains utility methods that manipulates strings. -
The
TimeUtilclass contains utility methods that are related to Time.
Documentation, logging, testing
Documentation
Style Guidance:
Diagrams:
For our developer guide diagrams, we use PlantUML. Here is a guide on how to set it up on Intellij.
Logging
Logging was performed to record whether Duke is initializing properly. Admittedly, this could be improved to record some of the more important operations. Implementation-wise, the current logging is designed to be scalable following AB-3.
Testing
This project has various tests that deal with different components and features of the application. The predominant types of test used for this project are Unit and Hybrid (Unit+Integration) tests.
Running Tests
- Method 1: Using the Intellij JUnit test runner
- Right-click on the
src/test/java folderand chooseRun 'All Tests' - To run only selected, right-click on the class or package and choose
Run 'TEST_NAME'
- Right-click on the
- Method 2: Using Gradle
- Open a console and run the command
gradlew clean test(Mac/Linux:./gradlew clean test)
- Open a console and run the command
Implementation
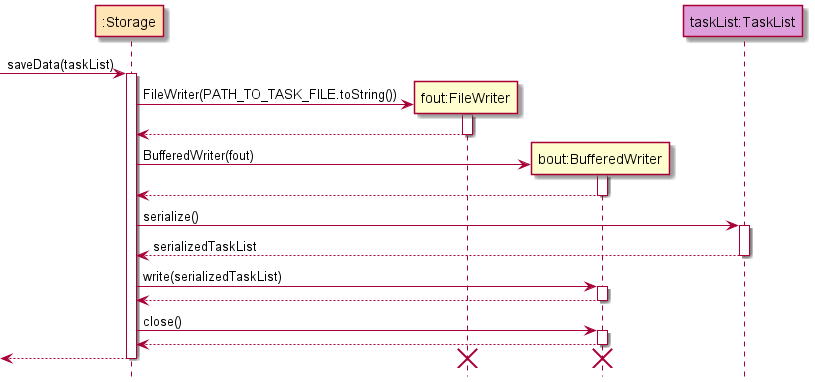
Saving data
- The path is determined based on the class type of the list given when calling the function.
- A FileWriter is created and subsequently used to create a BufferedWriter that points to the path.
- A taskList is called to return the serialized data of the list.
- BufferedWriter is used to write the serialized data into the location of the path.
- BufferedWriter is closed and the function subsequently returns.
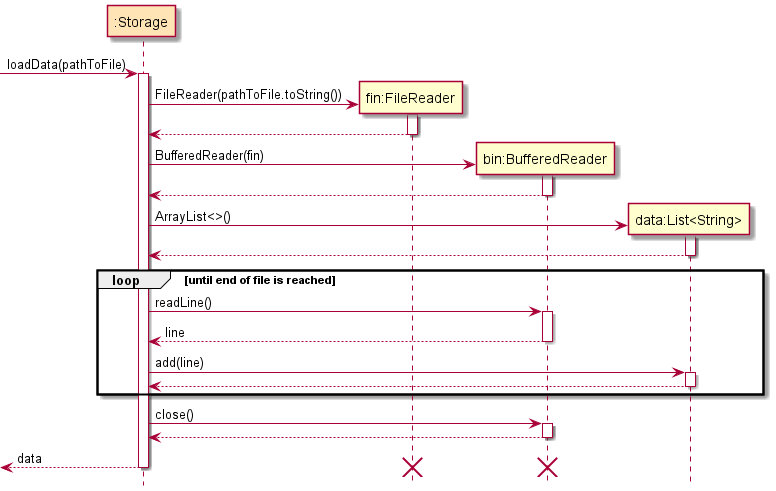
Loading data
- A FileReader is created and subsequently used to create a BufferedReader that points to the given path.
- An ArrayList of Strings is created.
- BufferedReader is used to read each line of data from the path and stored into the ArrayList. (with each item in the array representing 1 line in the file)
- BufferedReader is closed and the function returns the ArrayList containing the read data.
Save file formatting
Data for user added tasks, lessons and modules are stored in the task.txt, lesson.txt and module.txt files in the data folder respectively.
The format of the save files are as follows:
Tasks:
[Completion status] | [Task title] | [Day of the week] | [Priority] | [Information]
Completion status: “0” when not marked as done, “1” when marked as done.Task title: The full title of the task.Day of the week: The day of the week in full.Priority: The priority in caps. Possible priorities are low, medium and high.Information: The user given information for the task.
Example: 1 | CS2113 tP | Thursday | HIGH | Do Dev Guide
Lessons:
[Lesson title] | [Day of the week] | [Start time] | [End time] | [Lesson URL]
Lesson title: The full title of the lesson.Day of the week: The day of the week in full.Start time: The start time of the lesson. InHH:MM AM/PMformat.End time: The end time of the lesson. InHH:MM AM/PMformat.Lesson URL: The user given lesson url.
Example: CS2113 Tutorial | Friday | 02:00 PM | 04:00 PM | www.google.com
Modules:
[Module code] | [Module title] | [Number of MCs] | [Grade]
Module code: The module code of the module.Module title: The title of the module.Number of MCs: The number of modular credits of the moduleGrade: The grade assigned to the module.
Example: CS2113T | Software Engineering & Object-Oriented Programming | 4 | A-
Only a minimalist version of the module information is stored in the save file. This is because the full module information can be very detailed and lengthy, which would be impractical to be stored in full here. Hence, only the regularly used information for running the app is stored here.
Instead, detailed full module information will only be retrieved from the ModuleInfo.json file directly when needed.
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target Users:
NUS undergraduate students who prefer using a CLI application over GUI to manage their undergraduate activities and education.
Needs of users:
- Quickly manage and record tasks, lessons and modules
- Get module information of modules on demand
User stories
| Version | As a … | I want to … | So that I can … |
|---|---|---|---|
| v1.0 | user | add a task | keep track of my tasks |
| v1.0 | student | add a lesson | keep track of my lessons |
| v1.0 | user | list out tasks and lessons | see all my tasks and lessons |
| v1.0 | user | mark a task a done | keep track of completed tasks |
| v1.0 | user | delete tasks/lessons | keep my agenda clean |
| v1.0 | user | delete all tasks/lessons | quickly clear my agenda |
| v1.0 | user | store tasks/lessons in file(s) | retain data beyond the current instance |
| v1.0 | user | find tasks/lessons by keyword | quickly locate relevant information about tasks or lessons |
| v2.0 | user | attach priority to my tasks | see which tasks are of greater importance |
| v2.0 | NUS student | add/delete modules | keep track of my semester |
| v2.0 | NUS student | list out all the modules that I have with only the basic information | see all my modules with key information at a glance |
| v2.0 | NUS student | list out all the modules that I have with detailed information | see all my modules in detail |
| v2.0 | NUS student | search and browse for modules | look up for detailed information regarding a known module quickly |
| v2.0 | student | save and launch URLs for my lessons | quickly open my lesson URLs |
| v2.0 | student | see all my tasks/lessons for today or tomorrow | quickly see work that are upcoming soon |
| v2.0 | user | see all the commands the app offers | not have to constantly refer to the user guide |
| v2.0 | user | sort my task in order of importance | see the important ones first |
| v2.0 | NUS student | be able to keep track of my CAP score | gauge my current undergraduate performance |
Non-Functional Requirements
- The application should work on the major operating systems (Windows, Mac and Linux) if it has Java 11 installed.
- The application should be able to perform each command within 1 second.
- The application should allow users who are comfortable with typing to perform tasks faster than with on an application with a GUI.
Glossary
CLI: Command Line Interface
GUI: Graphical User Interface
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Testing commands for tasks
Adding a task
Test case: add task CS2113T assignment -d tue -i add feature -p low
Expected output: The task is successfully added and a message with the added task is displayed.
Adding a task without required flags
Test case: add task CS2113T assignment
Expected output: A message is displayed about missing flags in the input.
Adding a task with empty title
Test case: add task -d tue -i add feature
Expected output: A message is displayed that the title cannot be blank.
Listing all tasks
Test case: list task
Expected output: The full list of tasks is displayed.
Listing tasks sorted by priority
Test case: list task priority
Expected output: The full list of tasks is displayed, sorted according to the priority assigned for each task (HIGH, MEDIUM or LOW).
Listing tasks on a day of the week
Test case: list task tue
Expected output: A list of tasks on Tuesday is displayed.
Listing tasks with invalid day of the week
Test case: list task t
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the wrong format is used for the command.
Finding tasks with keyword
Test case: find task assignment
Expected output: A message is displayed with the tasks that contain the keyword.
Finding tasks with empty keyword
Test case: find task
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the wrong format is used for the command.
Marking a task as done
Test case: done task 1
Expected output: The task is successfully marked as done and a message with the task marked as done is displayed.
Marking a task with invalid index
Test case: done task 0
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the task entered is invalid.
Marking a task with an index that is not a number
Test case: done task m
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the task entered is not a number.
Deleting a task
Test case: delete task 1
Expected output: The task is successfully deleted and a message with the deleted task is displayed.
Deleting a non-existent task
Test case: delete task 0
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the task entered is invalid.
Deleting a task with an index that is not a number
Test case: delete task m
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the task entered is not a number.
Testing commands for lessons
Adding a lesson
Test case: add lesson CS2113T tutorial -d wed -s 11:00 -e 12:00 -l zoom.us/a19b3jkdjk93
Expected output: The lesson is successfully added and a message with the added lesson is displayed.
Adding a lesson without required flags
Test case: add lesson CS2113T tutorial
Expected output: A message is displayed about missing flags in the input.
Adding a lesson with empty title
Test case: add lesson -d mon -s 11:00 -e 12:00
Expected output: A message is displayed that the title cannot be blank.
Listing lessons
Test case: list lesson
Expected output: The full list of lessons is displayed.
Listing lessons on a day of the week
Test case: list lesson wed
Expected output: A list of lessons on Wednesday is displayed.
Finding lessons with keyword
Test case: find lesson tutorial
Expected output: A message is displayed with the lessons that contain the keyword.
Finding lessons with empty keyword
Test case: find lesson
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the wrong format is used for the command.
Deleting a lesson
Test case: delete lesson 1
Expected output: The lesson is successfully deleted and a message with the deleted lesson is displayed.
Deleting a non-existent lesson
Test case: delete lesson 0
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the lesson entered is invalid.
Deleting a lesson with an index that is not a number
Test case: delete lesson m
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the index of the lesson entered is not a number.
Launching a lesson with a URL
Test case: launch lesson 1
Expected output: The lesson’s URL is launched in a browser if it exists. Otherwise, a message is displayed stating that no link is provided.
Testing commands for modules
Adding a module
Test case: add module CS2113T
Expected output: The module is successfully added and a message with the added module is displayed.
Adding a module that is already in the list
Test case: add module CS2113T, then add module CS2113T again
Expected output: When attempting to add the module a second time, a message stating that the module has already been added is displayed.
Adding a module with an invalid module code
Test case: add module CS211
Expected output: A message stating that the module does not exist is displayed.
Listing modules
Test case: list module
Expected output: A list of all modules added is displayed.
Listing modules with details
Test case: list module verbose
Expected output: A list of all modules and their details is displayed.
Finding information for a module
Test case: find module CS2113T
Expected output: The module is successfully added and a message with information for the module is displayed.
Finding information for a module with an invalid module code
Test case: find module CS211
Expected output: A message stating that the module does not exist is displayed.
Deleting a module
Test case: delete module CS2113T
Expected output: The module is successfully deleted and a message with information for the module is displayed.
Deleting a module with invalid code or a module not in the list
Test case: delete module CS123
Expected output: A message is displayed stating that the module is not in the list.